obtain the scrollView's offset
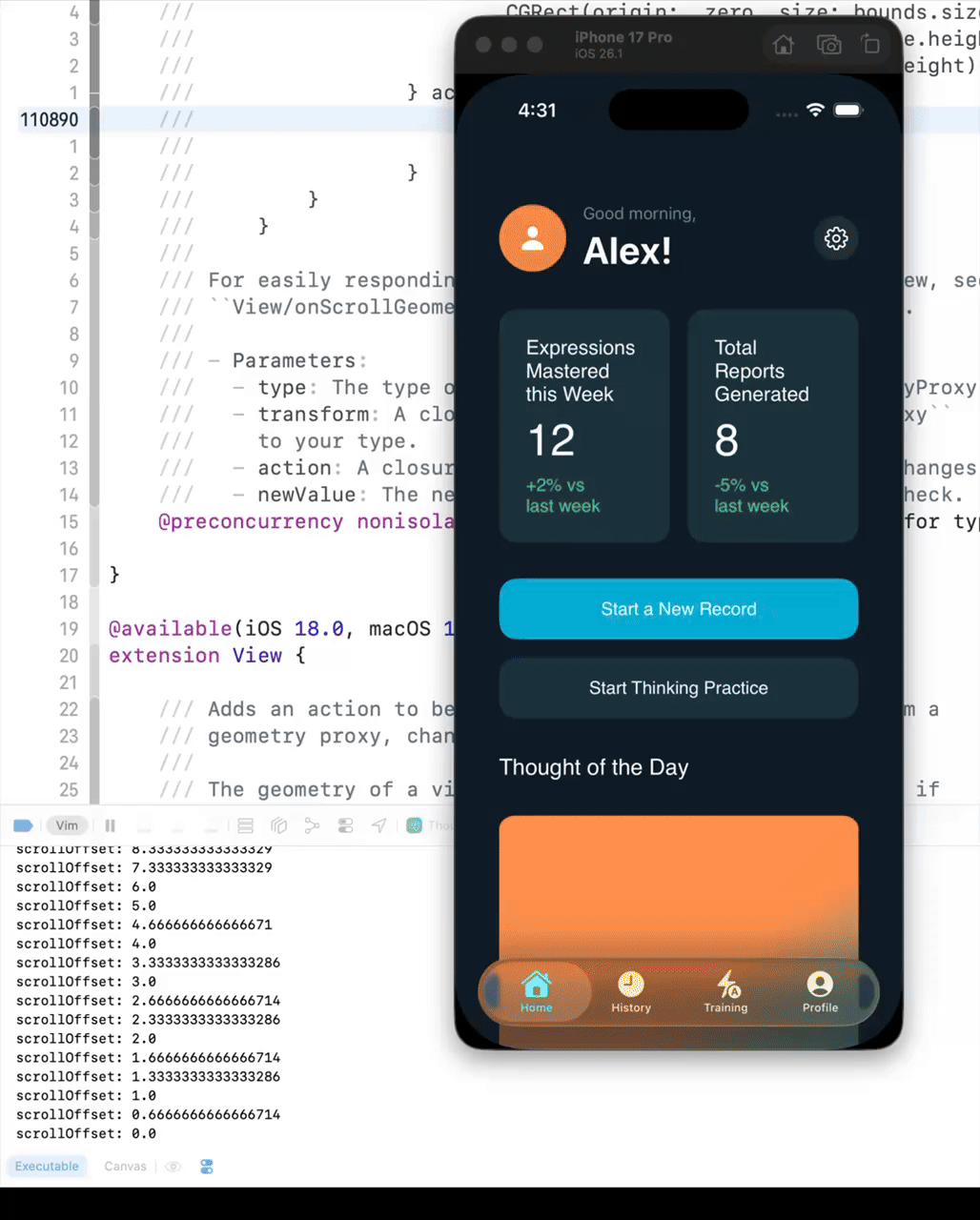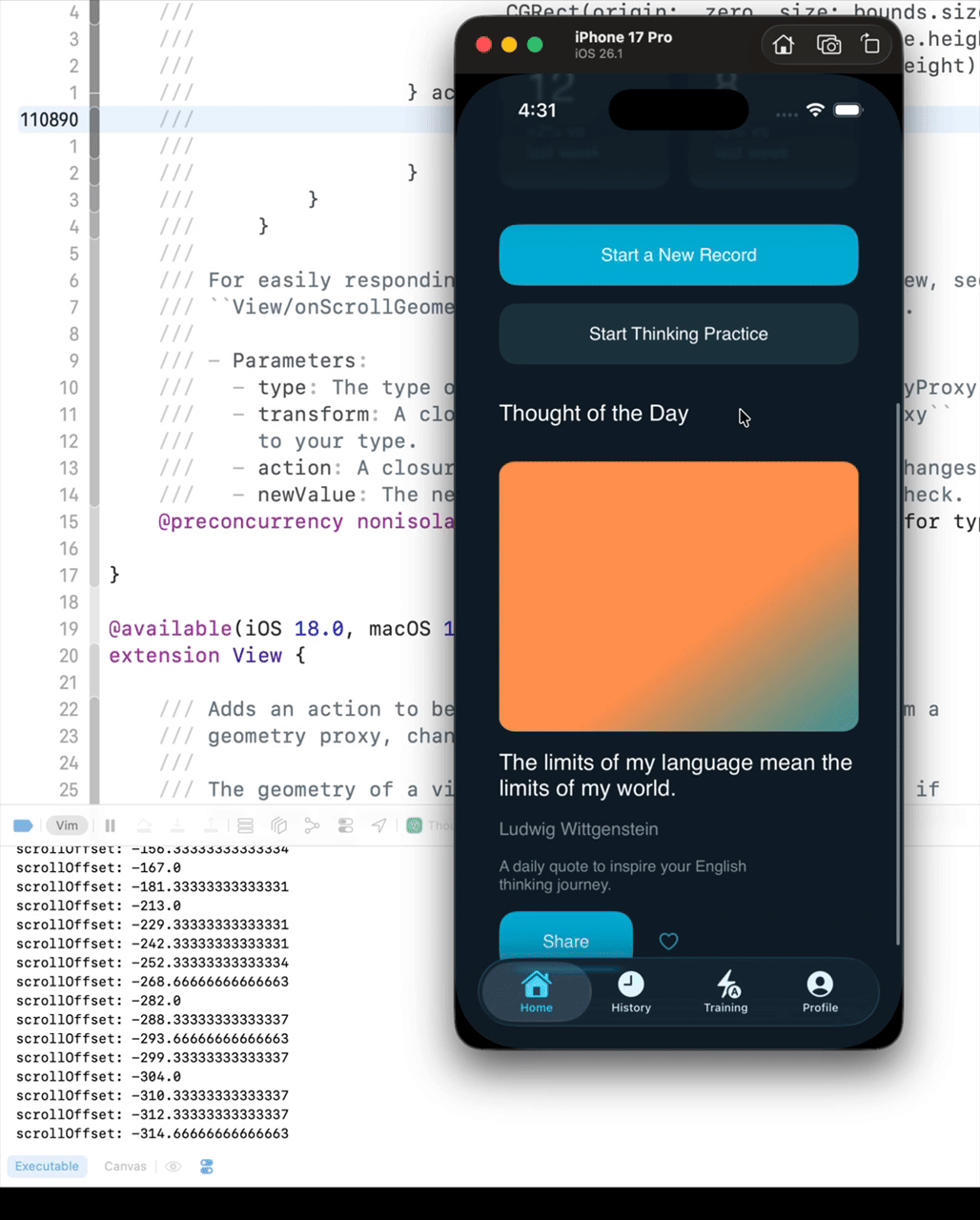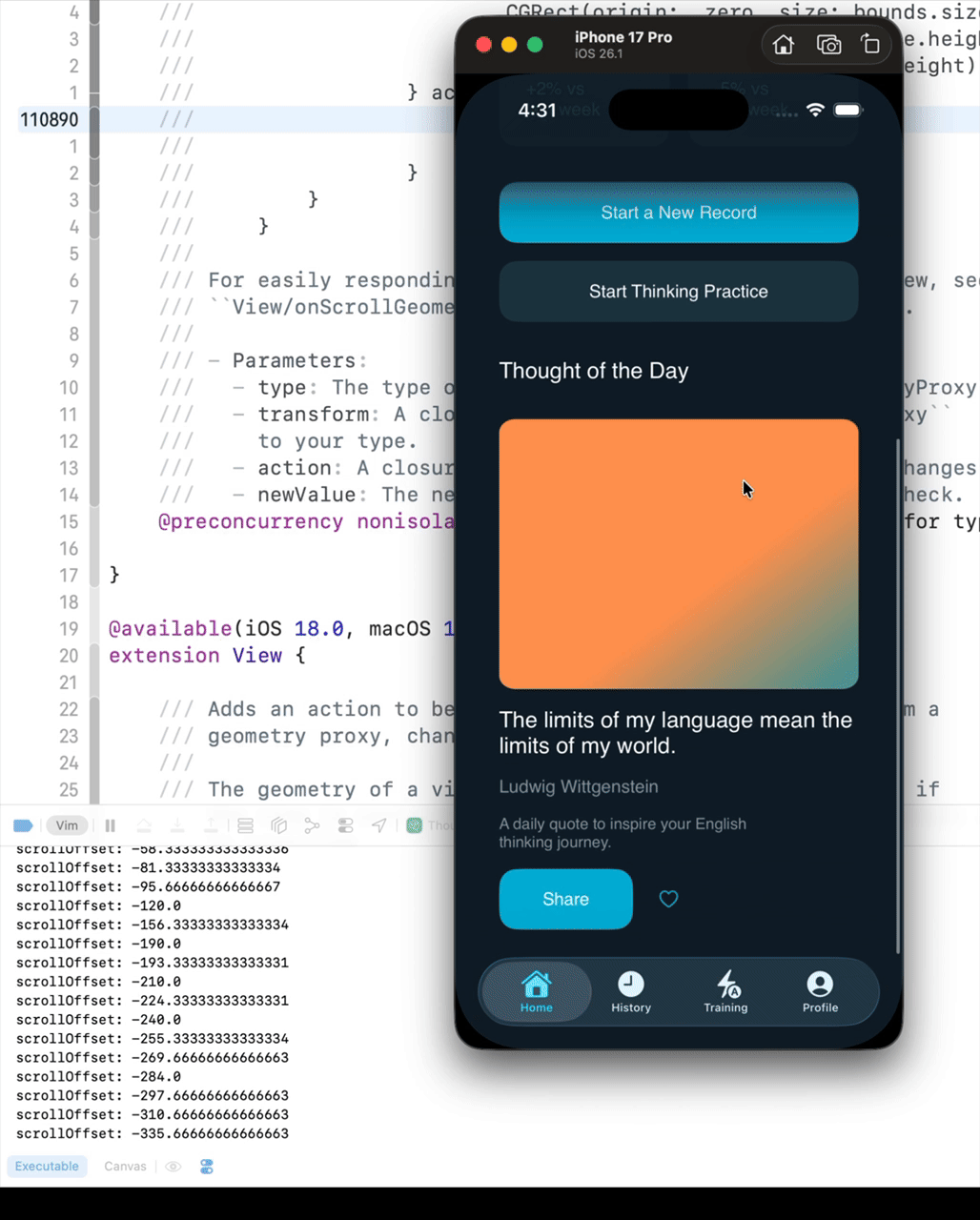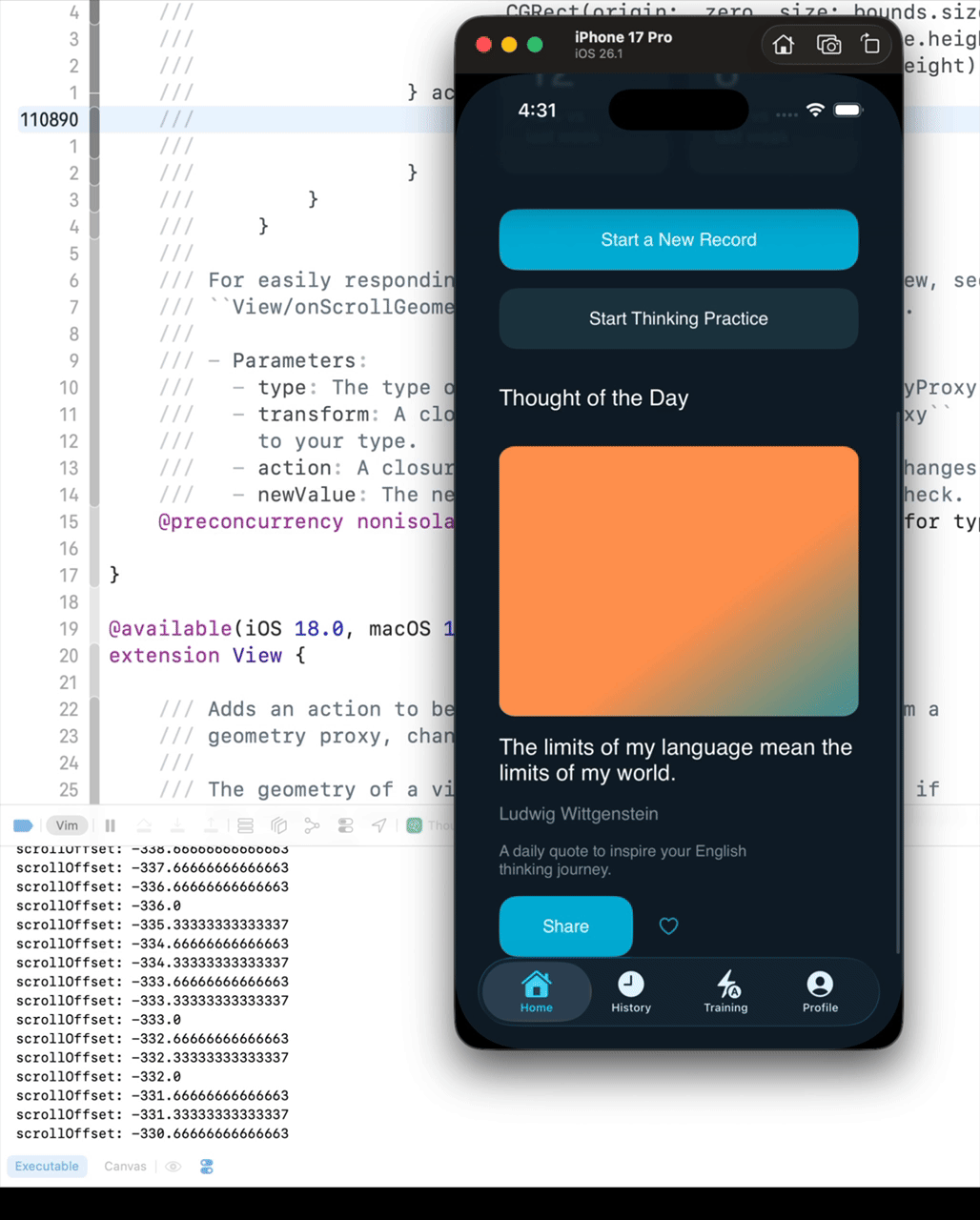
Before iOS 16, you could get the ScrollView’s offset using the following code. However, if the UI becomes complex, the scrollViewOffset will not update while scrolling.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
ScrollView {
VStack(alignment: .leading, spacing: 32) {
// 1. 将监测器独立出来,包裹在无间距的 VStack 中以避免布局干扰
VStack(spacing: 0) {
Color.clear
.frame(height: 0) // 占据 0 高度,不可见但存在
.background(
GeometryReader { proxy in
Color.clear
.preference(
key: ScrollOffsetKey.self,
value: proxy.frame(in: .named("scroll")).minY
)
}
)
LargeNavBarView()
.opacity(largeHeaderOpacity)
}
ContentArea
}
.padding(.horizontal, 24)
}
.coordinateSpace(name: "scroll")
.onPreferenceChange(ScrollOffsetKey.self) { value in
self.scrollOffset = value
}After iOS 16, you can reliably obtain the scrollView’s offset using the following code.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
ScrollView {
VStack(alignment: .leading, spacing: 32) {
// 1. 将监测器独立出来,包裹在无间距的 VStack 中以避免布局干扰
VStack(spacing: 0) {
Color.clear
.frame(height: 0) // 占据 0 高度,不可见但存在
.onGeometryChange(for: CGFloat.self) { proxy in
proxy.frame(in: .named("scroll")).minY
} action: { newValue in
self.scrollOffset = newValue
print("scrollOffset: \(self.scrollOffset)")
}
LargeNavBarView()
.opacity(largeHeaderOpacity)
}
ContentArea
}
.padding(.horizontal, 24)
}